Living a healthy lifestyle is important, and one aspect of that is maintaining a balanced diet. For individuals with hypertension, a low sodium diet is often recommended. Sodium, found in salt and various other foods, can raise blood pressure levels, potentially leading to serious health problems. By reducing sodium intake, individuals can better manage their blood pressure and improve their overall well-being.
Why is a low sodium diet important?
 A low sodium diet is vital for those with hypertension because it helps to lessen the strain on the cardiovascular system. Sodium can cause the body to retain excess fluid, which increases blood pressure. By reducing sodium intake, the amount of fluid retained is also reduced, resulting in lower blood pressure levels.
A low sodium diet is vital for those with hypertension because it helps to lessen the strain on the cardiovascular system. Sodium can cause the body to retain excess fluid, which increases blood pressure. By reducing sodium intake, the amount of fluid retained is also reduced, resulting in lower blood pressure levels.
Studies have shown a direct correlation between high sodium intake and hypertension. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends that individuals limit their daily sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams, and ideally aim for an even lower intake of 1,500 milligrams per day, particularly for those with hypertension or at risk for developing it.
Tips for a low sodium diet
 Adopting a low sodium diet may seem challenging at first, but with some simple tips and adjustments, it can become a sustainable and enjoyable way of eating. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
Adopting a low sodium diet may seem challenging at first, but with some simple tips and adjustments, it can become a sustainable and enjoyable way of eating. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
- Read labels: Be mindful of the sodium content in packaged foods. Many processed and pre-packaged foods are high in sodium, so opting for low sodium or sodium-free alternatives is a better choice.
- Choose fresh foods: Incorporate more fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet. These foods are naturally low in sodium and provide essential nutrients for overall health.
- Limit eating out: When dining out, it can be challenging to control the amount of sodium in your meal. Try to eat at home more often, where you have full control over ingredients and sodium levels.
- Experiment with herbs and spices: Enhance the flavor of your meals with herbs, spices, and other seasonings instead of relying on salt for taste. There are countless delicious combinations to try.
- Be cautious with condiments: Ketchup, soy sauce, and other condiments can be high in sodium. Look for low sodium or sodium-free versions, or try making your own healthier alternatives at home.
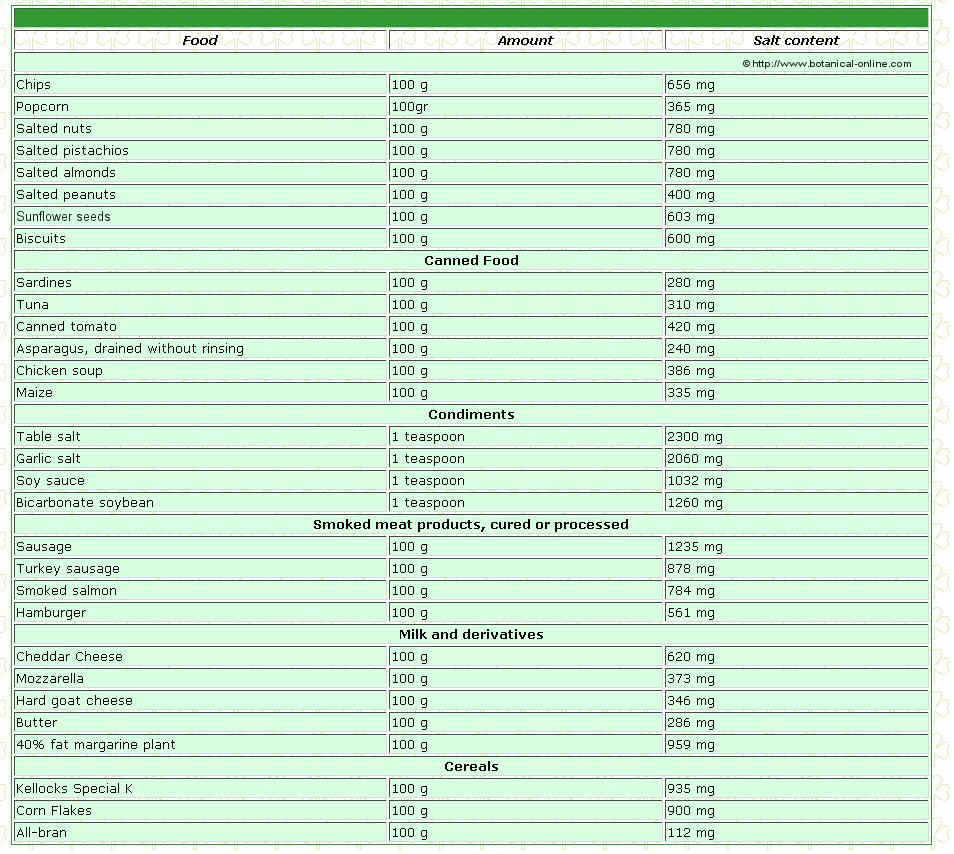
Understanding sodium levels in food
 It’s crucial to understand the sodium content in various foods to make informed choices for a low sodium diet. Here is a brief breakdown of sodium levels in common food categories:
It’s crucial to understand the sodium content in various foods to make informed choices for a low sodium diet. Here is a brief breakdown of sodium levels in common food categories:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables: Most fresh produce is naturally low in sodium, making them excellent options for a low sodium diet.
- Meats and poultry: Fresh cuts of meat and poultry are usually lower in sodium compared to processed or cured alternatives.
- Dairy products: Dairy products, such as milk and cheese, can be high in sodium. Opting for low sodium or sodium-free versions can help reduce your intake.
- Canned and processed foods: These often have high sodium content due to preservatives and additives. Look for low sodium or sodium-free options, or rinse canned foods to reduce sodium levels.
- Breads and grains: Bread, cereal, and pasta can contribute to sodium intake. Selecting low sodium options or preparing homemade versions can help control sodium levels.
- Snacks and condiments: Snack foods like chips and pretzels, as well as condiments like pickles and olives, tend to be high in sodium. Choose low sodium alternatives or consume them in moderation.
Creating a low sodium meal plan
 To make it easier to stick to a low sodium diet, planning meals in advance can be extremely helpful. Consider the following guidelines when creating a low sodium meal plan:
To make it easier to stick to a low sodium diet, planning meals in advance can be extremely helpful. Consider the following guidelines when creating a low sodium meal plan:
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in each meal.
- Choose lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, and legumes.
- Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, or whole wheat bread.
- Use herbs, spices, and other seasonings instead of salt to add flavor.
- Avoid processed and pre-packaged foods as much as possible.
- Prepare meals at home to have full control over ingredients.
By following these guidelines, you can create delicious and satisfying low sodium meals that contribute to better heart health and overall well-being.
Remember, adopting a low sodium diet is not an overnight process and may require some adjustments. However, with time and effort, it can become a sustainable and rewarding lifestyle choice. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and recommendations based on your specific health needs.
Make a commitment to your health today by reducing sodium intake and embracing a low sodium diet. Your heart will thank you!